指令
>> 表达式 ;:不显示运算结果(指令之后加上分号;,不显示计算结果。)
>> clc:清屏
算术运算
- 三角函数:sin(),cos(),tan()
- 开方:sqrt()
- 对数:log(),log2(),log10()
- e:exp(1)
变量
变量:大小写敏感,以字母开头,关键词不能作为变量名。声明方式:>> A=10
>> who:查看变量信息
>> whos:查看变量详细信息
>> clear Variable:移除变量Variable
>> clear:清除所有变量
变量优先级:
- Variable
- Built-in function
- Subfunction
- Private function: • MEX-file • P-file • M-file
关键词
| 预定义变量名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| ans | 计算结果变量名 |
| pi | Π |
| eps | 计算机最小数,当数字小于该值,认为为0(2.2204e-016) |
| inf/Inf | 正无穷 |
| NaN/nan | not a number,常为0/0、∞/∞ |
| i/j | 虚数单位,$\sqrt{-1}$ |
>> iskeyword:查看关键词
格式设定
| Style | Result | Example |
|---|---|---|
| short | Short, fixed-decimal format with 4 digits after thedecimal point. | 3.1416 |
| long | Long, fixed-decimal format with 15 digits after the decimalpoint fordouble values, and 7 digits afterthe decimal point for single values. | 3.141592653589793 |
| shortE | Short scientific notation with 4 digits after thedecimal point. | 3.1416e+00 |
| longE | Long scientific notation with 15 digits after thedecimal point fordouble values, and 7 digits after the decimal point for single values. | 3.14159265358979e+00 |
| bank | Currency format with 2 digits after the decimalpoint. | 3.14 |
| hex | Hexadecimal representation of a binary doubleprecisionnumber. | 400921fb54442d18 |
| rat | Ratio of small integers. | 355/113 |
>> format Style:设定数字显示格式
向量、矩阵
向量输入:
>> A=[1 2 3 4] $[1,2,3,4]$
>> A=[1;2;3;4] $\begin{bmatrix}1 \ 2 \ 3 \ 4\end{bmatrix}$
A = [
1 2 3 4;
5 6 7 8;
9 10 11 12;
]
$A=\begin{bmatrix}a_{11} & a_{12} & \cdots & a_{1n} \ a_{21} & a_{22} & \cdots & a_{2n} \ \cdots & \cdots & \cdots & \cdots\ a_{n1} & a_{n2} & \cdots & a_{nn}\end{bmatrix}$
矩阵元素:先行后列(元素从1开始)
A(1,2)=2
A(4)=2
A([1 2 4])=[1 5 2]
A([1,2;1,2])=[1 5;1 5]
A([1 2],[1 2])=[1 2;5 6]
//第1、2行和第1、2列的交集
Colon Operator
树
有向图、无向图
在 MATLAB 中,graph 和 digraph 函数用于构建表示无向图和有向图的对象。
创建图的主要方式包括使用邻接矩阵或边列表。
邻接矩阵
要在 MATLAB 中构建无向图,可以输入:
A = [
0 1 2;
1 0 3;
2 3 0
]
node_names = {'A','B','C'}
G = graph(A,node_names)
边列表
边列表通过列举边来表示一个图,但如果该图有断开的节点,边列表中将不会列出这些节点,需要单独指定它们。
在 MATLAB 中,边列表按列划分为源节点和目标节点。对于有向图,边的方向(从源到目标)很重要;但对于无向图,源节点和目标节点是可以互换的。
使用边列表构建该图的一种方法是,对源节点、目标节点和边权重使用单独的输入:
>> source_nodes = {'A','A','B'};
>> target_nodes = {'B','C','C'};
>> edge_weights = [1 2 3];
>> G = graph(source_nodes, target_nodes, edge_weights);
//起点、终点、(边的权值:可选)
下面可以创建一个有向图。s 和 t 中的对应元素用于定义图中每条边的源节点和目标节点。
>> s = [1 1 2 2 3];
>> t = [2 4 3 4 4];
>> G = digraph(s,t)
图的属性编辑、查看
构建图 G 后,可以通过G.Nodes 查看节点。通过将变量 Name 添加到 G.Nodes 表中来向图中添加节点名称。
>> G.Nodes.Name = {'First' 'Second' 'Third' 'Fourth'}';
也可以使用命令 G.Edges 查看边(源节点、目标节点、权值)。这些边在 G.Edges 中的顺序首先按源节点排列,其次按目标节点排列。对于无向图,索引较小的节点列为源节点,索引较大的节点列为目标节点。
>> P.Edges
ans =
6×2 table
EndNodes Weight
__________ ______
'A' 'B' 1
'A' 'C' 2
'B' 'A' 1
'B' 'C' 3
'C' 'A' 2
'C' 'B' 3
添加自定义属性
原则上,我们可以将任何变量添加到 G.Nodes 和 G.Edges 中,来定义图节点或边的属性。
例如,可以向 G.Edges 添加名为 Power 的变量,来指示每条边是 'on' 还是 'off'。
>> G.Edges.Power = {'on' 'on' 'on' 'off' 'off'}';
>> G.Edges
ans=5×3 table
EndNodes Weight Power
____________________ ______ _____
'First' 'Second' 10 'on'
'First' 'Fourth' 20 'on'
'Second' 'Third' 30 'on'
'Second' 'Fourth' 40 'off'
'Third' 'Fourth' 50 'off'
图节点 ID
默认情况下,系统会对使用 graph 或 digraph 创建的图的所有节点进行编号,编号从1开始。因此,可以通过数值节点索引(即编号)来引用它们。
如果图具有节点名称('A'),则还可以使用节点名称来表示图中的节点。因此,可以通过节点索引或节点名称来表示图中的已命名节点。
常用函数
图的常用函数如下:
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
addedge |
在图中添加一条或多条边 |
rmedge |
从图中删除一条或多条边 |
addnode |
在图中添加一个或多个节点 |
rmnode |
从图中删除一个或多个节点 |
findnode |
查找图中的特定节点 |
findedge |
查找图中的特定边 |
numnodes |
计算图中的节点数 |
numedges |
计算图中的边数 |
findnode |
查找图中的特定节点 |
findedge |
查找图中的特定边 |
添加节点
在G中添加五个节点
>> G = addnode(G,5)
G =
graph with properties:
Edges: [4x1 table]
Nodes: [9x0 table]
删除节点
删除节点 3、5 和 6,对图中剩余的六个节点重新进行编号,以反映新的节点数量。
>> G = rmnode(G,[3 5 6])
G =
graph with properties:
Edges: [2x1 table]
Nodes: [6x0 table]
添加边
使用 addedge 向 G 添加两条边。第一条边位于节点 1 和节点 5 之间,第二条边位于节点 2 和节点 5 之间。该命令将向 G.Edges 添加两个新行。
>> G = addedge(G,[1 2],[5 5]) //(图,起点,终点)
G =
graph with properties:
Edges: [4x1 table]
Nodes: [6x0 table]
删除边
使用 rmedge 删除节点 1 和节点 3 之间的边。。
>> G = rmedge(G,1,3)
G =
graph with properties:
Edges: [3x1 table]
Nodes: [6x0 table]
查找边
确定节点 1 和 5 之间的边的边索引。边索引 ei 是 G.Edges 中的行号。
>> ei = findedge(G,1,5)
ei = 2
查找节点
在图中添加节点名称,然后确定节点 'd' 的节点索引。数值节点索引 ni 是 G.Nodes 中的行号。
>> G.Nodes.Name = {'a' 'b' 'c' 'd' 'e' 'f'}';
>> ni = findnode(G,'d')
ni = 4
图的绘制
我们使用 plot 函数绘制 graph 和 digraph 对象。
默认情况下,plot 会检查图的大小和类型,以确定要使用的布局。
如果调用 plot 并指定输出参数,则此函数将返回 GraphPlot 对象的句柄。
随后,我们可以使用该对象调整绘图的属性。例如,可以更改边的颜色或样式、节点的大小和颜色等。
>> A = [
0 1 2;
1 0 3;
2 3 0
];
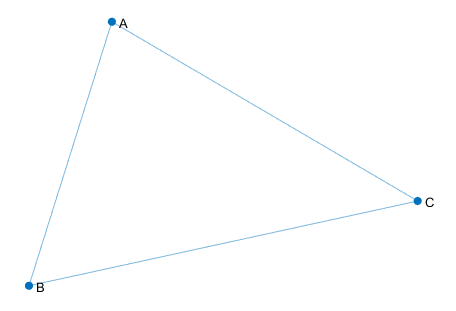
>> G=graph(A) //创建3x3无向图
>> G.Nodes.Name = {'First' 'Second' 'Third' }';//节点命名
>> p=plot(G) //绘图
同时,我们可以看到对象句柄的属性:
GraphPlot - 属性:
NodeColor: [0 0.4470 0.7410]
MarkerSize: 4
Marker: 'o'
EdgeColor: [0 0.4470 0.7410]
LineWidth: 2
LineStyle: '-'
NodeLabel: {'First' 'Second' 'Third'}
EdgeLabel: {}
XData: [-0.3454 -0.7305 1.0759]
YData: [1.0429 -0.8206 -0.2223]
ZData: [0 0 0]
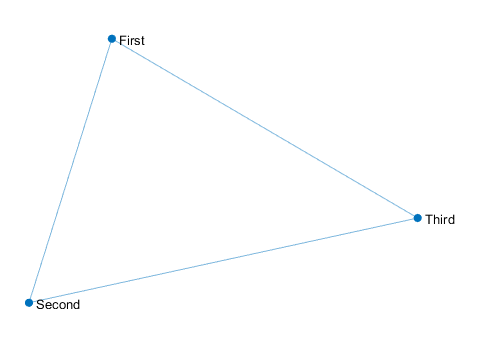
GraphPlot 属性控制所绘制图的外观和行为。通过更改属性值,可以修改图显示的各个方面。以下列出几个比较简单的属性,具体可查阅GraphPlot属性。
NodeLabel -节点标签,EdgeLabel-边标签:用于显示边、节点相关信息。
>> plot(G,'NodeLabel',G.Nodes.Name)
//将节点名称作为其标签
>> plot(G,'EdgeLabel',G.Edges.Weight)
//将边标签指定为权值(即显示权值)
ShowArrows - 切换显示有向边上的箭头,指定为 ‘on’ 或 ‘off’。
对于有向图,默认值为 ‘on’,即显示箭头,但您可以指定值 ‘off’,以隐藏有向边上的箭头。对于无向图,ShowArrows 始终为 ‘off’。
| 颜色名称 | 短名称 | RGB 三元组 | 十六进制颜色代码 | 外观 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
'red' |
'r' |
[1 0 0] |
'#FF0000' |
 |
'green' |
'g' |
[0 1 0] |
'#00FF00' |
 |
'blue' |
'b' |
[0 0 1] |
'#0000FF' |
 |
'cyan' |
'c' |
[0 1 1] |
'#00FFFF' |
 |
'magenta' |
'm' |
[1 0 1] |
'#FF00FF' |
 |
'yellow' |
'y' |
[1 1 0] |
'#FFFF00' |
 |
'black' |
'k' |
[0 0 0] |
'#000000' |
 |
'white' |
'w' |
[1 1 1] |
'#FFFFFF' |
 |
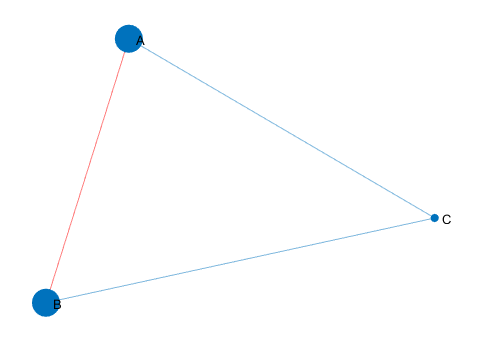
突出显示最短路径
以红色高亮显示沿此路径的边,并增大路径的节点的大小。输入如下:
p=plot(G)
highlight(p,[1,2])
highlight(p,[1,2],'EdgeColor','r')
绘图模板
A=[
1 0 3;
2 0 1;
3 3 1;
]
G=digraph(A,{'A','B','C'})
p=plot(G,'EdgeLabel',G.Edges.Weight,'LineWidth',0.5)
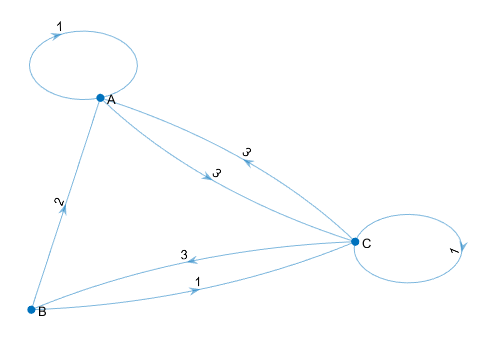
s = {'A','A','B'}
t = {'B','C','C'}
G = graph(s, t)
p=plot(G)